 The term neurofibromatosis, it summarizes a group of genetic diseases. Most often, the Neurofibromatosis Type 2 occurs type 1 (Recklinghausen’s disease), followed by neurofibromatosis. There are large differences in the clinical appearance between the individual shapes. Also within the respective type, there are various types of symptoms and the course of the disease. A causal treatment there is no.
The term neurofibromatosis, it summarizes a group of genetic diseases. Most often, the Neurofibromatosis Type 2 occurs type 1 (Recklinghausen’s disease), followed by neurofibromatosis. There are large differences in the clinical appearance between the individual shapes. Also within the respective type, there are various types of symptoms and the course of the disease. A causal treatment there is no.
Main feature of Neurofibromatosis Type 1 are changes of the skin. Are often pigmented lesions, known as Café-au-lait spots or milk coffee stains due to their dark brown color in infancy already. Also a summer shoots-like pigmentation of the armpits is common. Benign nodules in the skin, which are referred to as neurofibromas and occur mostly in childhood or during puberty are still typical. In some cases the manifestations of neurofibromatosis is limited to such skin problems, other other symptoms and complications are added, that can affect the eyes, bones, or the nervous system (such as epilepsy). The history of neurofibromatosis is hard to predict because the disease vary individually. However complications can be kept low by early diagnosis.
Main feature of Neurofibromatosis Type 2 are benign tumors that go out of the brain tissue and cranial nerves, so grow inside the skull. The growth of the tumors can lead to hearing problems, loss of balance, or a facial paralysis (Gesichtsnervlähmung). Skin problems are not as common as in type 1.
Neurofibromatosis (Recklinghausen’s disease): Definition
Are the two most important types of neurofibromatosis Neurofibromatosis Type 1 and Neurofibromatosis Type 2. They differ by their frequency and the present symptoms.
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 is also known in Recklinghausen-Applebaum disease or Crohn’s von Recklinghausen’s disease. The German pathologist Friedrich Daniel von Recklinghausen (1833-1910) described the typical of the disease skin tumors as first and demonstrated that they consist of nerve and connective tissue cells.
Neurofibromatosis Type 2 occurs less frequently than type 1 and manifests itself mainly in hearing and balance disorders, triggered by the growth of tumor on the auditory nerve.
Frequency
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (Recklinghausen’s disease) is one of the most common genetic disorders. About one of 3,000 newborns suffering from in Germany this type. Half of the diseases caused by new changes of genetic material (new mutations). For this reason, doesn’t have any disease within the family also found approximately 50 per cent of those affected.
With approximately 1: 40,000 new cases worldwide neurofibromatosis occurs type 2 less than the 1. new mutations are found here often.
Neurofibromatosis (Recklinghausen’s disease): Causes
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (Recklinghausen’s disease) is the result of a mutation of the neurofibromatosis 1 gene (NF1 gene). Neurofibromatosis Type 2 is caused by a mutation of the NF2 gene.
Both forms are inherited as an autosomal dominant trait. Autosomal is passed a genetic disorder, if the affected gene not an ZW but a so-called Autosome is located. The disease is passed then regardless of the gender of the parents to the child. Dominant means that it ill even if you by a parent a healthy gene and the diseased gene has got inherited from the other. The diseased gene is so to speak “stronger” than the healthy. In about half of cases of Neurofibromatosis Type 1 and type 2 is been inherited the mutation from a parent, but newly created (new mutation). There must be a family history so not in any case.
Neurofibromatosis (Recklinghausen’s disease): Symptoms
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF 1) and Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (NF-2) show very different symptoms. Also within a type, there are strong variations.
Neurofibromatosis Type 1
Characteristic symptoms
The first symptoms of Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (Recklinghausen’s disease) are usually pigmented lesions. The oval shaped, milchkaffeefarbenen patches (Café au-lait spots) and the summer shoots-like Sprenkelungen in the armpits and the groin area show around 80 percent of diseased infants in the first year of life. Also the oral mucosa may be pigmented.
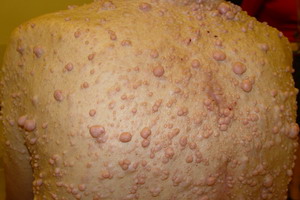
The characteristic neurofibromas arise later, often with puberty. Neurofibromas are benign tumors or nodules, which are composed of nerve and connective tissue cells. They are visible on the skin all over the body, can occur but also to internal organs and brain. Neurofibromas can be only erbsengroß – in other cases, they reach more than Palm-sized proportions. The nodules are coloured flesh usually not painful and generally to brownish. Sometimes, they shimmer bluish through the skin. Small neurofibromas arise regularly in the area of the front eye of the IRIS: where they are referred to as Lisch nodules.
Summary following symptoms are typical for the Neurofibromatosis Type 1:
- Pigmented lesions (Café au-lait spots)
- Sprenkelungen in the armpits and the groin area
- Neurofibromas
- English nodules
- Café au-lait spots (at least six)
Other symptoms
In addition to the characteristic symptoms of Neurofibromatosis Type 1, that occur in many cases more complaints can show up: frequently it comes to bone lesions, especially Wirbelsäulenverkrümmungen (scoliosis) – less sagging or false joint formations found on the Shin.
Other possible symptoms of neurofibromatosis can be type 1:
- Epilepsy
- Tumors on the optic nerve (Optikusgliome)
- benign nerve fiber tumors (Neuromas)
- Sensitivity disturbances (paresthesia)
- hormonal (endocrine) errors
- Learning problems (disorders of performance)
- Lack of concentration
- Neurofibromatosis Type 2
In neurofibromatosis 2 are different than rarely type 1 – neurofibromas of the skin and pigment changes type. The nerve tumors developing mainly in the Interior of the body, especially in the brain and in the area of the spine. English nodules occur never. The symptoms are often unclear and the actual underlying disease is diagnosed sometimes very late.
In almost all cases, tumors on the left and right auditory nerve (called Akustikusneurinome) are formed. Because the auditory nerve both forwards signals of the ear as also the Gleichgewichtsorgans to the brain, leads such a tumor to various symptoms that are typical for the NF 2: a reduction or loss of hearing, “Ringing” in the ears (Tinnitus), or problems with balance.
Hearing disorders
- Loss of balance
- Paralysis of the facial muscles (facial paralysis)
- Brain (cerebral Meningeoma)
- Cataracts (cataract)
Neurofibromatosis (Recklinghausen’s disease): Diagnosis
In Neurofibromatosis Type 1 can be then surely the diagnosis, when at least two of the following criteria are met:
- Café au-lait spots (six or more)
- Neurofibromas
- Freckles Sprenkelungen under the arms
- English nodules on the eye
- Tumor on the optic nerve (optic pathway glioma)
- Bone lesions, scoliosis
- Related first degree (father or mother) with neurofibromatosis type 1
On the basis of a blood sample, a neurofibromatosis can be diagnosed by a DNA examination is carried out. Here, the neurofibromatosis (NF-1 and NF-2) genes are tested for mutations out. Such a diagnosis can – be if identified the specific mutation in the family – even prenatally during pregnancy from childish cells (chorionic villi or amniotic fluid) (prenatal diagnosis).
So that stakeholders can be optimally supplied and accompanied it can be sometimes useful and helpful to consult so interdisciplinary, multidisciplinary. Depending on how much the disease is pronounced, it recommended is to consult a dermatologist, a neurologist and neurosurgeon, and a pediatrician. In some places, Office hours are offered, which specialize in such diverse advice.
Neurofibromatosis (Recklinghausen’s disease): Treatment
Neurofibromatosis can be treated not causally: the therapy is focused on individual symptoms. Disturbing and painful neurofibromas of the skin around can be removed with hyperuricemia in large numbers laser chirurgisch in neurofibromatosis.
Symptoms such as, for example, epilepsy, lack of concentration (in Neurofibromatosis Type 1) or Grauer Star (Neurofibromatosis Type 2) at, these are handled by the appropriate sections.
To recognize in time new tumors, it is advisable to take a medical examination to complete at least once in the year. This depends not only on the observation of the skin neurofibromas. There are also targeted internal organs, the eyes and the ears checked for neurofibromas.
Neurofibromatosis (Recklinghausen’s disease): History
The course is very different in neurofibromatosis. There is a wide range from harmless up to very severe forms. Through targeted and regular check-ups, most may recognize early complications and treated. This is essential to prevent possible complications of neurofibromatosis or to influence favourably during its course. Such complications are approximately Wirbelsäulenverkrümmungen (scoliosis), tumors (Optikusgliome) optic nerve or other brain tumors. Neurofibromas located under the skin may be associated – depending on the situation – with pain or neurological disorders, such as involvement of spinal nerves. A further complication is that epilepsy that can develop within a Neurofibromatosis Type 1.
Performance problems that may occur in connection with neurofibromatosis are an important aspect of the care of children. Performance problems speaking, if a child with learning problems are normal intelligence has. For the development of these children, it is important that a special promotion before the training is carried out.
Forecast
In most cases (about 60 percent), neurofibromatosis is a mild course – in principle she can be very different, even within a family. So, some of neurofibromatosis have type 1 affected only some pigmented lesions and neurofibromas, which sometimes are not perceived as signs of illness. Others, however, already exhibit tumors of the optic nerve or Cafe-au-lait spots to the birth. Also, it may be that only in the course of the time complaints develop, requiring treatment.
The risk of developing malignant tumours, is compared to the rest of the population both in Neurofibromatosis Type 1 as also in type 2 by about five percent neurofibromas increased, because degenerate to neuro fibrosarkomen or lymphomas develop can and.
Neurofibromatosis (Recklinghausen’s disease): Prevention
Because of neurofibromatosis is a genetic disorder, it is not possible to prevent the disease. Because of the possible complications, it is important, however, to establish the diagnosis as early as possible and carry out regular check-ups, so that in time a treatment of symptoms can be initiated.