 An eye with corneal Ulcer (Ulcus corneae) is flushed, hurts, is sensitive to light, water, looks not more as good and feels as a foreign body is penetrated. Who noticed these signs in itself, goes to the ophthalmologist best immediately or in a clinic.
An eye with corneal Ulcer (Ulcus corneae) is flushed, hurts, is sensitive to light, water, looks not more as good and feels as a foreign body is penetrated. Who noticed these signs in itself, goes to the ophthalmologist best immediately or in a clinic.
A corneal ulcer is damaged on the eye the cornea (cornea). Because the ulcer causing irregularities in the corneal surface and important for vision is the cornea as part of the optical system, corneal ulcers massively disrupt vision.
A corneal ulcer can have different causes: most common cause are bacteria; In addition also fungi, viruses and certain protists (Acanthamoebic) as pathogens are eligible. These pathogens can infect the cornea, however some favourable factors added must, for example:
- Contact lenses (especially soft)
- dry eyes
- superficial graze of the cornea (corneal erosion)
- Inflammation of Lacrymal
- Hornhautentzündung (mostly by herpes simplex)
- General factors that increase the risk of infection of a deficiencies:
- Diabetes mellitus
- rheumatic diseases (e.g. rheumatoid arthritis)
- HIV
- Alcoholism
- Malnutrition
- Drugs that suppress the immune system (so-called immunosuppressants)
- high age
A corneal ulcer is a basically serious eye disease: depending on which the Ulcus corneae emerged, can the condition of the eye very quickly (sometimes for hours) significantly deteriorate. In the worst case, the boil has holes in the cornea and an opening of the eyeball to the result; the affected eye can go blind. Therefore, a quick treatment is important for a corneal ulcer.
According to the most common causative agent usually antibiotics against a corneal ulcer are used. It is also important to eliminate the factors that have favoured the boil. This is also the most effective measure to prevent corneal ulcer: so, it is advisable, for example, to avoid bacterial accumulation can caused by clogged tear drop routes or by soft contact lenses. Just contact lens carrier which does not adequately maintain their lenses and too long, have a high risk to develop a Ulcus corneae.
Corneal ulcer: Definition
A corneal ulcer or corneal Ulcer (Ulcus corneae) is an eye disease marked by a damaged cornea, where it is on the edge of the corneal changes increasingly Einschmelzungen. Corneal ulcers (corneal ulcers) are caused by pathogens (infectious), which penetrate through superficial corneal injury. The affected eye is irritated and clearly flushed.
The cornea of the eye
The cornea of the eye (the cornea) is part of the optical system and plays a major role for the vision. Due to their strong refractive power, irregularities of surface affect how they (Ulcus corneae) exist such as the corneal ulcer, solid vision.
For their protection, the cornea of the eye is in a tight supply of irritation sensitive nerve. So can it be ensured that is injury of the cornea (which usually condition for this are that a corneal ulcer is created) make noticeable pain, convulsive eyelid closing, and lacrimation.
Corneal ulcer: Causes
A corneal Ulcer (Ulcus corneae) is due in an infection with a pathogen. For this infection to occur, must however, some favourable factors added. Among the factors that favour a corneal ulcer:
- dry eye
- Contact lenses (especially soft)
- superficial graze of the cornea (corneal erosion)
- Inflammation of Lacrymal
- Hornhautentzündung (mostly by herpes simplex)
- common factors that are associated with a higher risk of infection due to deficiencies of:
- Diabetes mellitus
- rheumatic diseases (especially rheumatoid arthritis can a so-called rheumatic corneal ulcer cause)
- HIV
- Alcoholism
- Malnutrition
- Drugs that suppress the immune system (so-called immunosuppressants)
- high age
Pathogens
(Ulcus corneae) that can penetrate as agent to different underlying causes, a corneal ulcer usually through a superficial corneal injury, which can be very small, in the cornea:
Bacteria:
Most common triggers of corneal ulcers are bacteria. In the temperate regions mainly staphylococci, pneumococci, A Streptococcus and Pseudomonas underlie aeruginosa a corneal ulcer causes.
General common causes for bacterial corneal ulcers are the acute inflammation of the lacrimal sac and the tears away reduction, or the tear-away closure: If the trails of tears are constricted, can there according to bacteria accumulate. Also paralysis individual nerves in the face and eye area, which lead to a missing or too rare eyelid closing, or an eyelid Malposition (e.g., entropion) can cause of superficial lesions to a corneal ulcer, if pathogens in the eye. In younger people are often (polluted or too long worn) contact lenses for the bacterial corneal ulcer responsible; in higher age, however, the boil is more immune deficiency (diabetes mellitus, chronic alcoholism).
Mushrooms:
More rarely, fungi are (e.g. Candida albicans) based on a corneal ulcer causes. Again, contact lenses are in younger people a common excitation source and an immune deficiency occurs in older people often.
Viruses:
A corneal ulcer can have its causes in an infection with viruses. Usually, a Hornhautentzündung by herpes simplex for the emergence of viral corneal ulcers in mind is responsible. More frequent viral pathogens are varicella zoster virus (the virus of shingles) or adenovirus.
Amoeba:
In addition to bacteria, fungi and viruses, certain single-celled organisms than pathogens for a corneal ulcer are eligible: the so-called Acanthamoebic. These amoebae can be found, for example, drinking water or in the contact lens container and penetrate through minor injuries of cornea.
Corneal ulcer: Symptoms
A corneal Ulcer (Ulcus corneae) raises usually significant symptoms: are typically:
- a striking pseudo-fibrosis eye
- severe pain,
- a distinctive foreign body sensation
- Photophobia,
- Lacrimation and
- a compromised vision.
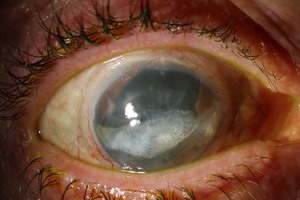
In addition, the conjunctiva is often swollen by a corneal ulcer. Also on the cornea are to recognize symptoms: the corneal ulcer himself shows up as grauweiße turbidity in the cornea; the edges are thrown up, the Centre is diluted. In the anterior Chamber of the eye, a different strong stimulus State prevails corneae in a leg.
If the corneal ulcer but is developed in the context of rheumatic disease (rheumatic Ulcus corneae), little inflammatory symptoms and hardly any complaints occur on the eye.
Corneal ulcer: Diagnosis
A corneal Ulcer (Ulcus corneae) the diagnosis is usually easy to make. Usually indicates the history (history) of the persons concerned (contact lenses, weakened immune system, previous eye injury, etc.) on a possible corneal damage. The doctor through an examination of the eyes at the slit lamp can confirm the suspicion of a corneal ulcer in which ulcers are usually clear. When a corneal ulcer, it is advisable to rinse always the trails of tears, to exclude that these are constricted.
A corneal ulcer is available, various tests are needed for further diagnosis to determine the causes of sore and to initiate appropriate treatment. To do this, the ophthalmologist first takes a smear of the conjunctiva of the eye and the base of corneal ulcer. May be it is possible to prove causative bacteria in these samples. If it turns out that bacteria pathogens of chancroid are corneae, it is necessary to determine its resistance (resistance to certain antibiotics) for the optimal treatment.
Corneal ulcer: Treatment
When a corneal Ulcer (Ulcus corneae) is first and foremost a local therapy. In addition, it is advisable that you eliminate the factors which have encouraged the creation of corneal ulcer for the successful treatment: do you have, for example, narrow paths of tears, can be best just to treat these. If you are contact lens carrier, you do not necessarily on wearing of contact lenses, as long as the corneal ulcer is not completely healed. If an insufficient eyelid closing has led to the corneal ulcer, it is may be necessary to temporarily close the eyelids through an operation.
Most of the time bacteria for an ulcer are responsible corneae. Then, antibiotic eye drops used come to local therapy. If you have a medium-sized eye inflammation (Uveitis) may, in addition to the corneal ulcer – a so-called systemic is only occasionally (the entire organism related) need treatment with antibiotics (e.g. in the form of tablets). It is important to proceed as quickly as possible against the corneal ulcer. If the agent is not yet complete contact resources that cover all eligible as bacteria (so-called broad spectrum antibiotics) therefore the antibiotic treatment first. As soon as the outcome of smear and the causal organisms are not fixed, your doctor can switch to, where appropriate, the treatment on a targeted product.
A quickly advancing corneal ulcer or perforated cornea, it is advisable to treat the perforated cornea rapidly operationally – therapy can consist, for example, in a corneal transplant (keratoplasty). In the acute stage of the disease of the eye, it is possible, however, that the transplanted cornea not good heals up, so that subsequent operations may be needed.
Against the rare by fungi (e.g. Candida albicans) conditional corneal ulcer come to local therapy according to Antipilzmittel (so-called antimycotics) in the form of eye drops or eye ointments used. A corneal ulcer caused by viruses also a systemic administration of drugs (e.g. acyclovir) may require in addition to the local treatment.
Local treatment with eye drops is first of all a hervorgerufenenen by certain single-celled organisms (Acanthamoebic) corneal ulcer. The treatment of Ulcus corneae can however weeks drag, without success, so that often surgical measures are necessary. It is important that the corneal transplant this set takes place before the amoebas to the wheel of the cornea can wander and infect the graft from there again.
An operation is at the hard-to-treat rheumatic corneal ulcer also often to the treatment used. But even after a corneal transplant relapses can form (i.e. the Rheumatoid related ulcers can occur again).
Even if left behind scars in cornea after a healed from corneal ulcer which significantly affect eyesight, this can be through a corneal transplant resolve.
Corneal ulcer: History
A corneal Ulcer (Ulcus corneae) is an eye disease of basically serious to nehmendem course: depending on which originated the corneal ulcer, the condition can deteriorate very quickly – sometimes within clearly hours. If it is possible to stop the boil by the drug therapy, a scar – so a clouding of the cornea – lags. Depending on where these corneal opacity is and how big it is the vision of the affected eye is impaired.
If the corneal ulcer in the worst case in the remainder of the holes the cornea, the outcome of disease – also in emergency surgery – is often fatal. Vision can be more clearly affected then as a result of Ulcus corneae; Sometimes the eye affected by the boil can go blind completely.
Corneal ulcer: Prevention
(Ulcus corneae) you can prevent a corneal ulcer, you prevent possible corneal damage. You can do this, for example, when insufficient eyelid closing by regular treatment of the eyes with ointments. It is also advisable to avoid seed collections that can arise through clogged tear paths or by wearing soft contact lenses. Generally, it is particularly important that you carefully maintain your Haftschalen and clean if you are contact lens carrier. Wearing the contact lenses never too long – especially not during the night.
A complete protection against skin ulcers is not possible because you can prevent all corneal damage: unforeseen accidents or foreign bodies can cause small corneal injuries – and the corresponding germs that will penetrate and cause a corneal ulcer, occur almost everywhere in the environment.