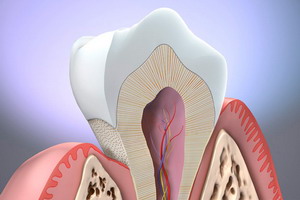
 The teeth as part of the soft body are anchored in the Oberkiefer-and Unterkieferknochen of the teeth keep tissue. Teeth serve the food intake and fulfil an important function of advance in the nutrition as food shredder. The structural components of teeth are differentiated based on the simplified representation.
The teeth as part of the soft body are anchored in the Oberkiefer-and Unterkieferknochen of the teeth keep tissue. Teeth serve the food intake and fulfil an important function of advance in the nutrition as food shredder. The structural components of teeth are differentiated based on the simplified representation.
Cross section of a tooth for a larger view please click on
A tooth can be divided into a visible and an invisible section that is located in the bones in the oral mucosa. In a healthy state, the visible part of the tooth consists of the so-called inlay. The longer part of a tooth, is this hidden consisting of Zahnhals (under the gums) and tooth which is connected to the so called tooth restraint apparatus with the jaw. There is one wurzelige teeth, such as the incisors, and multiple wurzelige teeth, such as the molars; While the back teeth of the upper jaw usually three roots have that of the lower jaw two roots.
Tooth enamel
The enamel is an almost pure mineral layer which covers the Crown as the outermost layer. The enamel is very hard and is used to protect of the tooth against external harmful influences, as well as in particular the protection against abrasion. The enamel is to 95% by weight obtained from minerals (mainly phosphate and calcium), a percent of the organic components (proteins) and four percent of water. The effect of fluoride on the enamel inserts in the prevention of tooth decay (caries prophylaxis). Fluoride forms larger crystals with correspondingly reduced pore volume, improved regular reproduction of the mineral layer (remineralization) and positive effect on the plaque metabolism.
Zahnbein (dentin)
The Zahnbein (dentin) is located under the tooth enamel. This includes not only the Crown area, but also the root zone, or the dental pulp. Here, the dentin in the melting range (mantle dentin) differs structurally from the dentine in the field of dental pulp (pulpales dentin). The so called dentin tubules that contain partial Nervenzellfortsätze, have a different density; pulpa close, they are in a higher density. Especially the Seitenkanälchen of mantle dentins are also increasingly permeated by a clear liquid. In contrast to the tooth enamel as the pure mineral adjustment operations are possible in the dentine in the form of stimulating dentin, channel calcification, and fluid shifts (to a limited extent). This property is related to the increased proportion of organic components in the Zahnbein, which consists to 20% by weight of organic matter and 70 percent from minerals and 10% from water. Due to these ingredients, the dentin is also softer than the tooth enamel.
Cement
From the transition zone of the Crown to the tooth covered a mineralised tissue, the dental cement, the surface of the tooth root. The dental cement contains no nerves or vessels and anatomically belongs not to the tooth itself, but to the tooth restraint apparatus (Parodont). Other elements of the tooth restraint apparatus are the teeth bones, connective tissue and the mucous membrane.
Dental pulp
The dental pulp, the core area of the tooth, the tooth body has cells, blood vessels and nerve fibres. Distinction in spatially Crown and root pulp, which however organic form a unit. Healthy teeth, which include an intact tooth body, are as alive or vital referred to, i.e. they react to external stimuli, such as, for example, cold. In diseased teeth inflammation can spread through this system to the bone of root tips area (Pulpitis).
The dentition
The human dentition different types of teeth composed of, their respective anatomical characteristics, just on root length and number of, therapeutic measures have to be considered:
- Incisors: chisel-shaped, with simple root
- Canines: with dreikantiger cutting Crown and long tooth root
- Premolars: front grinders, zweihöckriger Crown and a root
- Molars: large back teeth with Crown; four to five höckriger the molars of the upper jaw three have which of the lower jaw two roots
The dentition of children (primary) consists of 20 teeth, the teeth of adults from 32 so-called permanent teeth (including wisdom teeth).
The following types of teeth are present in the adult dental:
- 8 Incisors
- 4 Canines
- 8 Premolars
- 12 Molars
FDI system
There is a specific system to the exact name of the teeth, the FDI system. While a number is, associated based on a simple principle, each tooth. The teeth are numbered starting with the right half of the upper jaw, from the front incisor to the rear Backenzahn.