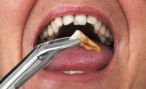
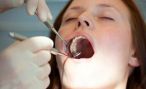
Dental extraction is the removal of a tooth from the mouth. Extractions can be best practices for several reasons. The principal is tooth decay that has destroyed enough tooth structure to not be able to restore it. Included teeth, including wisdom teeth are also taken routinely.
Dental extraction is the removal of a tooth from the mouth. Extractions can be best practices for several reasons. The principal is tooth decay that has destroyed enough tooth structure to not be able to restore it. Included teeth, including wisdom teeth are also taken routinely.
Types of extractions
Simple extractions (exodonties) are performed on teeth that are visible in the mouth, that are not excessively damaged by decay and that can be retrieved without complication. The dentist moves the tooth with a roller, under local anesthesia, and then remove the tooth.
Surgical extractions (odontectomies) involve the teeth that are not easily accessible, that have very curved root or which are substantially destroyed by decay. The dentist is the gum around the tooth and bone. The tooth can be separated into several pieces before extraction and stitches maintain the integrity of the gingiva during healing.
Possible complications
Infection dentist may prescribe an antibiotic necessary.
Bleeding extended in the healthy subject the bleeding stops 3 to 4 minutes after extraction, but flow or blood seeps occur during 48 hours. The bleeding can be controlled through a gauze of cotton on the extraction site and by closing the mouth to create pressure. A wet tea bag can also replace cotton since the tannic acid in tea helps the formation of a clot. Avoid spit or rinse for the first 24 hours to not dislodge the clot and cause an Alveolitis. The research of hemorrhagic history personal or family, as well as acting on hemostasis treatments are to search before any dental extraction.
Pain there may be pain for a few days: must then be the pain that the dentist has prescribed or that he was advised to take.
Swelling if extraction has been complicated il il may be a swelling of the face or even a change in colour on the skin.
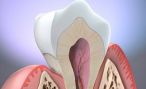
Alveolitis following the extraction of a tooth, with movements of bone crushing or burning (poorly cooled strawberry) alveolar bone can be injured creating an Alveolitis. This situation is characterized by intense pain, a bad taste in the mouth and sometimes a difficulty opening the mouth. It is accentuated by smoking. Alveolitis is a temporary situation that lasts a few days and can be mitigated by the dentist by affixing a soaked lock of eugenol.
Paresthesia very rarely during dental extraction, the nerve is affected, causing a loss of sensitivity especially at the level of the language or the lower teeth. Paresthesia occurs especially when the extraction of wisdom teeth. The loss of sensitivity is rare and usually temporary, though exceptionally it may be permanent.