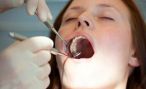
A tooth extraction – called by medical professionals tooth extraction – is the desired removal of a tooth from the mouth.
A tooth extraction – called by medical professionals tooth extraction – is the desired removal of a tooth from the mouth.
Most people can their first losses usually still remember: the teeth are solved almost by itself, were somehow out gewackelt and radiant presented to the parents.
On the other hand, enormous respect exists before removal of wisdom teeth. But this doesn’t have to be: the extraction of wisdom teeth is one of the most common dental operations and complications are rare. Usually, the corresponding body is healed after a few days.
At the tooth extraction, the dentist removes a tooth from his bone specialist by mechanical pulling out. Dentistry uses mostly pliers and lever to loosen the tooth and to solve. Whether the tooth extraction is rather fast and easy or harder, where appropriate, feasible, influence the location and strength of the tooth, the shape of its root, the bone structure and the surrounding neighboring structures.
Reasons for a tooth extraction
Deciduous teeth
The natural loss of a Milchzahns is due to the later following breakthrough of a second and permanent tooth. This resolves the smaller milk tooth from the bottom piece by piece, so that the root in the optimal case completely disappears. The root loss makes it possible the relatively low-pain out shake of a first tooth, because the tooth is not more deeply anchored in the bone. Only the mucosa is maintaining the milk tooth in the mouth. Runs the tooth loss not as planned by nature, the dentist helps to. This can be the case to promote the faster Zahndurchbruchs wrong growing out permanent teeth and inflamed or carious primary teeth.
A milk tooth shall remain basically in place, until his successor comes out. A former tooth extraction (tooth extraction) can be necessary if the milk tooth from caries or following an accident is heavily destroyed. In exceptional cases, teeth on the advice of Orthodontists can be removed to create a better starting position for the growing permanent teeth.
Second teeth
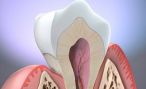
Permanent teeth are no longer so easy to remove. The bone has become fixed – especially in the lower jaw, it has a compact outer layer. The roots are longer and the rear molars by their majority at roots wide surface anchored in the bone.
A tooth extraction can have many reasons:
- A tooth decay is too far advanced.
- A disease of the teeth holding apparatus (periodontal) has caused too much relaxing or partially grow out the tooth.
- Inflammation of the nerve of the tooth has affected the bones and do not heal.
- A large jaw cyst has made of the root tip.
- The tooth is broken badly.
- The teeth should be cleaned up before radiotherapy in cancer.
- For lack of space in the jaw, tooth extraction helps to correct gearing of dentition.
When unplanned tooth extraction, a strong relaxation of a tooth, as well as stinging or pressing at the bite pain evidence suggests that the dentist must remove the affected tooth. The doctor provides a preliminary diagnosis by touch using of fingers and probes. The definitive decision, he manufactures to often Additionally an X-ray of a tooth.
Wisdom teeth
The tooth extraction (tooth extraction) can be complicated for Weisheitszähnen because the teeth have partially angled roots and are more difficult to achieve at the back of the mouth. Often it’s necessary going to cut parts of the bone or to cut out a piece of bone (osteotomy). This is, for example, required if the dentist in the bone must remove this tooth or tooth remnants such as roots.
Reasons for a necessary distance of Weisheitszahns are for example:
- Lack of space
- Errors of the adjacent tooth
- Inflammation
- Pocket or cyst formation
If the dentist on the growth of Weißheitszahns (e.g. in the x-ray image) young patients recognize that the tooth could later lead to such problems it can be convenient to remove the tooth before the age of 25. At this young age, there is less complications. However, should the doctor in an individual case carefully, whether the preventive removal of a tooth, which makes no complaints yet, outweighs the risk of the intervention.
Approach to the tooth extraction
Before the tooth extraction (tooth extraction) certain high-risk patients (e.g., people with weak immune systems or heart disease) need to take antibiotics, to avoid infections. If the suspected a blood clotting disorder, a blood collection and, where appropriate, treatment of bleeding disorders are made
At the tooth extraction pain are rather low, because the tooth is made schmerzunempfindlich before surgery using local anesthesia. Only the first child’s teeth, which are not very schmerzempfindlich due to their construction, a tranquilizer injection is sometimes unnecessary. You have to have a local anaesthetic during a tooth extraction, so you can participate – if you have taken any additional pain or sedative – still on the road.
With special instruments, the dentist loosens up the tooth before removing him from his tray of bone using a pair of pliers or a lever. Then, he carefully cleans the bone and inserts a sponge in the bone. Finally, he made the oral mucosa of the wound site. The dentist removed the sutures after intercurrent healing, usually seven days later.
Complications
Immediately after the tooth extraction can cause difficulty in feeding.
Ongoing bleeding can cause problems after a tooth extraction. Tabled sponges, tight seams, and using a bite are, which put pressure on the wound area, able to fill but also more bleeding.
Should that infect the wound, it is important to clean the wound and to take antibiotics or soaked strips of fabric into the wound. An infection leads to a delayed healing process. The development of cysts after the procedure is possible. Rare complications include the fracture of the jaw, the breaking into the maxillary sinus and damage to the adjacent tooth.
The extraction of Weisheitszähnen it – can occur very rarely, that nerves are injured. Lengthy unconscious and taste disorders may occur. Optimal operational planning on the basis of X-rays and necessary in individual cases close cooperation with an oral surgeon to prevent such complications.
In the elderly, or if teeth have been reinstated after an accident (Replantation), it is possible that the tooth is held no longer by his teeth holding apparatus but is continuous (ankylosis) directly with the bone. In this case, the dentist can no longer simply pull the tooth, but must drill him lavishly out.
Healing after tooth extraction
The dentist gives you after the tooth extraction (tooth extraction) special advice to the behavior in the following days: he explains how long you should eat nothing and whether Mouthwashes are useful. Both depend on the performed operation. Usually the doctor are also analgesic drugs you with on the way.
On on alcohol, nicotine, caffeine and tea you should not generally as long as possible, but at least a day long, to ensure a good healing. A cooling – for example with a wrapped cooling Pack – reduces the swelling.
Swelling with slight limitation of mouth opening, slight pain and bruising are subject to generally any special treatment and sound off within a few days. The complaints are so strong that painkillers are necessary, so should be avoided containing acetylsalicylic acid (ASS), as this ingredient can encourage a bleeding.
Prevention
Optimal dental care and oral hygiene is the best way to avoid a tooth extraction. Each individual tooth is valuable and should be obtained therefore if possible. He could later anchor or pillar for a dentures serve as. Through the various methods of tooth preservation, it is now possible to preserve even a heavily damaged tooth over years and decades. Only when all other treatment options have been exhausted, a tooth extraction is advisable.