If narrow fear makes: people with a claustrophobia can not stay in tight, closed or crowded spaces or difficult to endure. Whether lift, solarium, a full cinema or the underground – there are many situations which can become a nightmare with claustrophobia. The good news: you can get A claustrophobia with professional help well under control!
If narrow fear makes: people with a claustrophobia can not stay in tight, closed or crowded spaces or difficult to endure. Whether lift, solarium, a full cinema or the underground – there are many situations which can become a nightmare with claustrophobia. The good news: you can get A claustrophobia with professional help well under control!
16 Floors are to deal with – and with two heavy grocery bags: A lift is a great help for most people in this situation. Finally they save stairs of lots of and the lift carries equal with the purchases. An elevator is convenient.
A person who suffers from claustrophobia thinks entirely differently. Regarding an upcoming trip with the elevator, he felt great fear. In his mind, thoughts revolve as:
- “I will choke or faint.”
- “The elevator is stuck and no one will help me.”
- “I can not escape in case of emergency and delivered.”
Whether lift…
The fear within a claustrophobia can be associated with various physical symptoms, for example with sweating, trembling, or heart palpitations. The fear is too large, the Klaustrophobiker is prefer, for example, the staircase and the elevator avoid.
The fear of the elevator is only an example of a typical situation that scares a Klaustrophobiker. The problem – and sometimes even larger rooms that are very crowded, so that one feels restricted are closed, close rooms. Some people with claustrophobia have only fear specific situations such as such as the elevator ride, others are afraid all narrow premises.
… or solarium: people with claustrophobia have fear of confined spaces.
Not everyone who suffers from claustrophobia, must necessarily be in treatment. Some people with claustrophobia are restricted in their everyday life, however, so much that a therapy is necessary. In particular the behavioral therapy has proven itself in the treatment of claustrophobia: where the person concerned learns specifically to suspend the situation and to withstand the fear – as long as the fear subsides.
Prevent you can’t a claustrophobia – however you should not hesitate to seek professional help at first possible sign.
The previously handled a claustrophobia, the higher is the chance again to get rid of these.
Claustrophobia: Definition
A claustrophobia is an anxiety disorder, where inappropriate fear is narrow and closed rooms at the heart. Some Klaustrophobiker are also afraid of (larger) spaces, in which very many people close to densely reside and where the air is bad, so that a feeling of narrowness can arise. The name claustrophobia is derived from the Latin term claustrum (= closure, cage) and the Greek nickm (= fear, anxiety) off.
Include to typical situations that can make a Klaustrophobiker fear, for example:
- the stay in the lift
- the investigation in a MRI (MRT)
- the stay in the full department store
- the stay in transportation such as airplane or subway
- the stay in crowded areas, such as in the disco or in the cinema
A claustrophobia is one of the specific phobias. A specific phobia is a unreasonably strong fear of specific objects or situations, for example before dogs, blood, spinning – or just closed / tight spaces, as is the case with the claustrophobia. Specific phobias such as a claustrophobia are widespread.
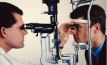
Problem for some Phobics: a Magnetresonanztomograph
Klaustrophobien may occur also in the context of agoraphobia. People with agoraphobia fear, in specific locations or in certain situations during a possible panic attack, no escape to have or they are afraid to get no help in case of emergency. The fears occur, for example, in crowds, public places or travel – may concern but also confined spaces so claustrophobic fears may also include the image of an agoraphobia.
In the some people use also the term agoraphobia, if they feel claustrophobia. This is however not correct – because a claustrophobia is exactly the opposite of a claustrophobic, so the fear of wide squares. Rather, fears arise with Klaustrophobikern, if they must go in tight, enclosed spaces, for example in an elevator. Could thus be called rather a claustrophobia fear of space.
Fear in the MRI
For people with claustrophobia, an investigation into a closed MRI (MRT) is similar to a nightmare: Minutenlang – often even longer than half an hour – she must remain in the narrow tube. Many Klaustrophobiker cancel the investigation or succeed only with drugs to overcome their fear. An open Magnetresonanztomograph can remedy: scientists have discovered that most people feel less fear when the power is on the side open. Therefore, the researchers request to improve the quality of equipment and the closed to prefer the half-open devices.
Claustrophobia: Causes
A claustrophobia can have different causes. Rather, some people develop a claustrophobia than others. Thus, several factors must come together. What causes exactly for a claustrophobia eligible, there about each approach different doctrines. In particular the learning-theoretical point of view moves in the search for the causes of claustrophobia in the foreground.
Learning-theoretical approach
Representatives of the learning theory approach assume that a phobia in a stepped process is developed – so also the claustrophobia.
In a first step “a person learned” the fear of enclosed spaces. Later, he eschews the situations which, in turn, strengthened the fear.
For example, A man lives in a high-rise building and drives daily easily with the elevator. The man had a lot of stress in recent months and is therefore very tense and easy to bring in the version. One day the fully staffed elevator between two floors gets stuck and it takes two hours, until the passengers are free. During the span of the elevator, the man suddenly erupts in panic; He fears to get no air, suffering from sweating, and begins to tremble. He feels the situation wants to shipped only in the open. Back outside he feels relieved and the symptoms sound off. He does not explain itself, the sudden symptoms. Also, he sees no connection to the previous stress. Due to these unexplained symptoms, he is insecure and gets even more fear.
The next day, fears the man the elevator could again get stuck – and chooses the stairs from now on. In the future, situations which have to do with elevators, attempting to avoid. The man has learned that the situation “Elevator ride” is associated with anxiety and subjective threat. Would he again sit out the situation, he can dismantle probably fear. Because he avoids them but he has still maintained his fear. In the course of the disease fear to similar situations can widen, for example on driving in the subway.
This learning effect occurs but not for everyone – by far not everyone who has stuck in an elevator suffers then a claustrophobia. Rather must join other factors in order to actually develop a claustrophobia. It is important, for example, how much a person on anxiety symptoms such as sweating and trembling respects and assessed them. The person concerned may not agree such complaints; He takes them as potential danger was what strengthened the physical anxiety symptoms – so that the fear is even stronger. A vicious circle is created; through the many symptoms that arise solely by the fear, the Klaustrophobiker it sees confirmed that something will happen him to.
Psychoanalytic approaches
In psychoanalytic theories, one takes the view that people with phobias such as a claustrophobia are shifting their internal conflicts to the outside. This approach assumes that the Phobics not really is afraid narrow and enclosed spaces, but that his fear for an unconscious fantasy is symbolically related to confined spaces in combination. The visible anxiety so actually stands for an inner anxiety.
Neurobiological aspects
Researchers dealing with the neuro-biological aspects of an anxiety disorder as the claustrophobia, assume that you only then developed a phobia if it is particularly vulnerable. Therefore, not only environmental conditions play a role, but also as an individual component, for example a genetic disposition (disposition).
Scientists suspect that the autonomic nervous system of anxiety patients from birth is particularly fragile and easily aroused, so that the persons especially rapidly feel fear. The autonomic nervous system controls and regulates the functions of internal organs, such as the breathing. Also, the balance of different messengers in the brain plays a role (e.g., serotonin, norepinephrine, gamma-aminobutyric acid), which durcheinandergerät in anxiety patients.
Moreover, it seems the limbic system, a certain part of the brain, to exhibit differences compared with the non-anxious people. The limbic system is important for the processing of emotions.
Claustrophobia: Symptoms
You can identify a claustrophobia because, that the person concerned will show specific symptoms. People with claustrophobia fear in tight, closed rooms, as for example in the lift or in the Metro. Some stakeholders are afraid only in the elevator others in turn in all tight spaces.
While in a tight, closed room, people with claustrophobia often show symptoms that occur in other phobias.
These include:
- strong feelings of anxiety and the panic
- Heart palpitations, heart-pounding
- Sweats
- Tightness in the chest
- Tremble
- Nausea
- Feeling to get no air
- Urination, Stuhldrang
- Feeling of being near a fainting
The Klaustrophobiker feared losing control. He is afraid that, in an emergency, no escape route available is (e.g. in the closed lift or in the subway). The data subject believes to die, choking, are powerless, or go crazy. He wants only one thing: as soon as possible to escape the situation.
People with claustrophobia although know that their fears are unreasonable, can the symptoms but still not prevent.
But even outside of the actual situation, such symptoms may occur such as at the sole thought because to enter an elevator or at the sight of an image of a closed room.
For fear of the situation, the Klaustrophobiker begins to shun them. So he chooses the stairs instead of the elevator, for example, in the future, or he shoves her an upcoming MRI investigation is because he is afraid of the confinement in the investigative unit. Later, more and more cases of this avoidance behaviour can be affected so that the daily life of the person concerned may be severely limited.
The avoidance behavior is typical of a phobia.
Claustrophobia: Diagnosis
To secure the diagnosis on suspicion of claustrophobia, the doctor or psychologist asks first for complaints. In addition he will want to know when the symptoms occur and whether the fear of certain situations or objects is bound for example to elevator ride.
The subject’s help in the diagnosis.
It is important to know how strong the symptoms are and how long they last. Using this information, the expert can find out whether there is a pure claustrophobia or whether a different disease the cause is, for example an agoraphobia.
A tool for the diagnosis of a claustrophobia may be a so-called anxiety diary. There are clearer about the patient and his complaints the therapists and may facilitate the experts, better to plan the treatment procedure.
Claustrophobia: Treatment
Many people who are affected by claustrophobia, are not in therapy. Sometimes the claustrophobia is only slightly pronounced or but the person concerned can handle easily the anxiety-producing situation, so that his life is not impaired.
A Klaustrophobiker feels extremely burdened by his fear, or he is severely restricted in his everyday life he should think about a therapy.
Behavioral therapy
In particular the behavioral therapy has proven to treat of a claustrophobia.
A promising treatment of claustrophobia is the behavioral therapy. At the beginning of the treatment the therapist explains how his illness arose from learning-theoretical view the Phobics. There are several methods that are used in the behavioral therapy.
The systematic desensitization aims to reduce the fear gradually in a relaxed environment. The patient together with the therapist determines the hierarchy. Then relaxes the person concerned and introduces himself to the situation that makes him the least fear. Step by step more and more situation added while in therapy, first in mind, later in reality.
In the exposure process, the therapist specifically confronted those affected with anxiety filled situation. So the patient consists, for example, specifically the situation of “Elevator ride” – until fear subsides significantly and he realizes that he no fear must have. If he only sees the elevator or even driving, depends by the progress of treatment and the intensity of fear.
In the cognitive behavioural therapy gives the person concerned of psychology, what thinking patterns cause that fear is maintained. Goal is to change this mindset during the treatment.
More treatment options
It helps some people with claustrophobia to learn a relaxation technique. Targeted relaxation can help to remain calm even in a fear-filled situation and become a total eligible – but it requires some patience and practice. Common relaxation techniques include the progressive muscle relaxation according to Jacobson or autogenic training.
In self-help groups for people with anxiety disorders, sufferers can talk openly and without shame about their problem. Exchange among like-minded people are out support each other.
Very great fear, the doctor can prescribe medication. So-called benzodiazepines have a calming effect, may be but only in the short term used, because they can depend on. In particular if the claustrophobia in the context of another disorder such as for example the agoraphobia, also Antidepressants can be prescribed.
A further treatment option is to find out what internal conflict underlying the fear in a psychotherapy. The person concerned should learn better to deal with his fears and to deal with a potentially unresolved dispute or to handle better with him.
Claustrophobia: History
The course can look different in a claustrophobia. Many people with a claustrophobia can avoid the anxiety-producing situation and feel not restricted in their daily lives. While some affected the phobia itself sounds off, others require a treatment.
For fear of the situation, the Klaustrophobiker begins to shun them. Later, you can fear spread and increase in intensity. Even staying on a public toilet can be used to the anxiety trap, because the closed door could clamp – so the fear of Phobikers. As a result, social life can suffer so that the person concerned is losing quality of life. Some Phobics access to drugs or alcohol to keep anxiety producing situations, but run the risk of becoming dependent on. Therefore, it is important to get help if you have the feeling to no longer meet the problem in time.
The prognosis in the treatment of claustrophobia is mostly favourable. The earlier the treatment does, the better!
Claustrophobia: Prevent
You can not directly prevent a claustrophobia. If however, you notice that you have increasingly fear the stay in closed, tight spaces such as an elevator, a subway, or a full cinema, you should seek timely professional assistance. Because: The previously handled a claustrophobia, the chance again to get quickly to the disease is greater!
An anxiety disorder as the claustrophobia is not what you ought to be ashamed. The longer you wait, the more you must overcome themselves, to deal with the fears. Therefore: better in time to the doctor, rather than unnecessarily to suffer!