 The acute tonsillitis is an infection of the tonsils (tonsillitis acuta, angina tonsillaris). Agent of tonsillitis are mostly bacteria (especially A streptococci), rare viruses.
The acute tonsillitis is an infection of the tonsils (tonsillitis acuta, angina tonsillaris). Agent of tonsillitis are mostly bacteria (especially A streptococci), rare viruses.
An acute tonsillitis is throat and swallowing pain, swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck, fever and a strong feeling of illness. The acute, usually purulent tonsillitis the chronic tonsillitis is to differentiate, which makes often little complaints. Children and young adults are most commonly affected by a tonsillitis.
If you think that you have an acute tonsillitis, you should see a doctor. This recognizes after some simple research quickly, whether it is an acute or chronic tonsillitis. In some cases, he performs a throat swab to determine the responsible agent and suspected a chronic tonsillitis. Next, the doctor sets the appropriate therapy.
Treatment consists in a tonsillitis initially from the pain and fever medication use. As a home remedy, Wadenwickel can help to reduce the fever.
A chronic tonsillitis (tonsillitis chronica) requires usually an operation in which a surgeon surgically removed the tonsils (so-called tonsillectomy). This can improve the quality of life of the person concerned. Is the starting point of infection (so-called infection) is removed, this can greatly reduce the risk for STREP complications of other organs.
In the context of a tonsillitis also complications are possible. It is an acute tonsillitis, the almonds in rare cases can increase strongly. Shortness of breath can be the result. Caution is warranted especially in children, whose Mandeln are already enlarged in a healthy state (so-called tonsil hyperplasia), since this can make breathing difficult.
For a chronic tonsillitis complications by germs are possible, because due to the chronic infection, bacteria are constantly available.
You can however only indirectly prevent a tonsillitis. Through regular sports and a balanced and vitamin rich diet to strengthen your immune system. This minimizes the risk of a tonsillitis.
Tonsillitis (tonsillitis, angina tonsilaris): definition
The tonsillitis (tonsillitis, angina tonsillaris) differ between the acute and the chronic tonsillitis can:
The acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis acuta) is usually a bacterial caused sudden inflammation of the tonsils. A chronic tonsillitis (chronica tonsillitis), however, means that the tonsils are permanently inflamed by bacteria. It caused only a few or no complaints. The acute tonsillitis occurs mainly in children and young adults.
Anatomy
Oral cavity
The tonsils are located on the transition from the oral cavity to the pharynx between the front and rear Gaumenbogen. You are responsible to train the immune system in the first years of life, in addition to other organs and tissues of the body. The body thereby learns to fend off foreign and harmful substances. These include above all viruses and bacteria.
The tonsils (tonsils) are getting bigger from the first to the third year of life. With the start of puberty they form is back gradually. Then, the almonds will exert no crucial function. In the case of a chronic tonsillitis they do little for the immunity already at pre-school age. On the contrary, they represent an ideal breeding ground for Bacterial colonization and chronic infection. At this stage, it is sometimes useful to remove the tonsils. This entails mostly no complaints.
Tonsillitis (tonsillitis, angina tonsilaris): causes
An acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis acuta) are the causes usually in infections caused by certain bacteria strains. These bacteria are especially streptococcal of Group A (short: A Streptococcus). Other bacteria such as staphylococci, pneumococci and Haemophilus influenzae can be the trigger. A weakened condition or a deficiencies favour a tonsillitis. Causes for a weakened immunity, stress or additional diseases are eligible.
An acute tonsillitis occurs more frequently, it can lead to a chronic tonsillitis. The chronic tonsillitis (chronica tonsillitis) are the causes in a lasting inflammation of the tissue of the almond. Products of bacteria and dead cells deposited in lining wells (Crypts) of almond tissue and thus ensure ongoing inflammation of the tonsils. This scarred and rugged adipose tissue, making further progress of the tonsillitis.
Tonsillitis (tonsillitis, angina tonsilaris): symptoms
Differ depending on whether a tonsillitis (tonsillitis, angina tonsillaris) acute or chronic runs, is also the symptoms.
The acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis acuta) is expressed mostly by increasing pain in the upper neck. Swallowing as well as the opening of the mouth, such as yawn, the pain can radiate up to the ears out. In addition are often general symptoms such as malaise, headache and fever. In many cases, the saliva production is increased and the voice sounds occupied.
Some diseases appear much like a tonsillitis, because they cause some of the same symptoms. These include the Pfeiffersche glandular fever (Mononucleosis), Scarlet fever, diphtheria, herpes Angina and angina Plaut Vincenti.
At the chronic tonsillitis (tonsillitis chronica) rarely acute symptoms are. Sometimes slight difficulty swallowing or an unpleasant taste and bad breath occur. In addition, a chronic tonsillitis may express by symptoms such as a reduced performance and concentration. The cervical lymph nodes may be swollen permanently, without however causing pain. Not infrequently, a chronic tonsillitis is accompanied by repeated flare-up of acute tonsillitis.
A tonsillitis may trigger diseases. Bacteria of the almonds can settle on the basis of other organs or alerted immune cells begin to attack “incorrectly” body tissue. Thus, there may be inflammation in other organs. Rheumatic fever with possible participation of the heart, joints and skin, as well as a nephritis are examples of such diseases – that occur but after a tonsillitis only in rare cases.
Tonsillitis (tonsillitis, angina tonsilaris): diagnosis
On suspicion of a tonsillitis (tonsillitis, angina tonsillaris) the doctor makes the diagnosis usually quickly after some brief research.
Acute tonsillitis
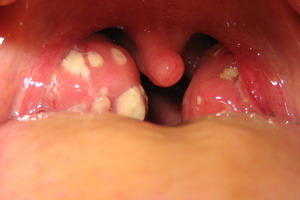
In the acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis acuta) the doctor provides diagnosis, he looks into the mouth of the patient. Reddened and swollen tonsils, as well as any facilities pads on the surface (so-called facilities Stippchen) considered to mark an acute, purulent tonsillitis. If the doctor scans the neck often leads to pain in the area of swollen lymph nodes, providing an additional indication of a possible tonsillitis. At the same time can the Gaumenbögen flushed and the tongue occupies be.
When a tonsillitis are therefore mostly as view diagnostic. A blood test is usually not required. A throat swab to determine the responsible agent is necessary only in individual cases and in cases of suspected a chronic tonsillitis.
Chronic tonsillitis
The chronic tonsillitis (tonsillitis chronica) characterized by scarred modified almonds. The tonsils can be both reduced and enlarged. At pressure of pus or a crumbly mass (decay products of cells, so-called detritus) can empty them themselves. Erhärten can the diagnosis by a smear from the surface of the almond and the detection of antibodies against the relevant pathogens in the blood.
Tonsillitis (tonsillitis, angina tonsilaris): treatment
When a tonsillitis (tonsillitis, angina tonsillaris) therapy depends on the course and the complaints.
Acute tonsillitis
In the case of an acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis acuta) treatment consists first of using pain and fever medicines
If you are suffering from a tonsillitis, record only food, which is soft and not highly seasoned. Cold drinks or ice alleviate the difficulty swallowing. Drink as much as possible and avoid this fruit juices, because their acids in addition to irritate the inflamed tonsils and throat burn. You should avoid also milk. As water with very little or no carbon dioxide and herbal teas are recommended.
Because smoking worsens the symptoms of tonsillitis, you should avoid this. It takes about one to two weeks, until an acute tonsillitis is completely cured.
In acute or frequently occurring tonsillitis, the doctor for the treatment prescribes an antibiotic, usually penicillin. The antibiotic accelerates the healing process, but not always can prevent that the symptoms get worse and eventually forms a collection of facilities (abscess). This can happen if the therapy is used too late or the antibiotic against this kind of bacteria is not suitable. A timely Antibiotikaeinnahme means that possible complications about less form of heart or kidneys. When complications, as well as in the case of multiple recurrent tonsillitis an ENT specialist can remove surgically (Mandeloperation, tonsillectomy) the almonds.
Home remedies for acute tonsillitis
A tonsillitis often anti-inflammatory and disinfectant monger solutions with Sage or Chamomile help as a home remedy. Such solutions are suitable for a tonsillitis for therapy of accompanying symptoms such as such as the sore throat. As well, they support the actual healing process… Also Wadenwickel have proven home remedies to reduce fever. When a tonsillitis, analgesic lozenges temporarily mitigate the difficulty swallowing; Home remedies such as warm or dry neck wrap can do, well you about. Although such treatments often shorten the duration of a tonsillitis, but home remedies are often useful to relieve the symptoms.
Chronic tonsillitis
In the case of chronic tonsillitis (tonsillitis chronica) is the most promising treatment is surgery to remove the tonsils (so-called tonsillectomy). So those affected no longer have ongoing disease and to Kämpfen-further tonsillitis, the starting point of infection (so-called infection) is removed, this can greatly reduce the risk of strep complications of other institutions.
Tonsillitis (tonsillitis, angina tonsilaris): history
Forecast
An acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis acuta) has generally a good prognosis. You heal for no outcome in appropriate treatment after a duration of about one to two weeks, while a chronic tonsillitis (tonsillitis chronica) permanently remain. The removal of the tonsils usually improves symptoms, the general condition and health status and thus the prognosis here only.
Complications
A tonsillitis possible complications. It is an acute tonsillitis, the almonds in rare cases can increase strongly. Shortness of breath can be the result. Caution is warranted especially in children, whose Mandeln are already enlarged in a healthy state (so-called tonsil hyperplasia), since this can make breathing difficult.
For a chronic tonsillitis (tonsillitis chronica) complications by germs are possible, because due to the chronic infection, bacteria are constantly available. Therefore, the inflamed tonsils may be starting point for secondary diseases. So there can be in a tonsillitis caused by Streptococcus following rheumatic fever, kidney or Herzentzündungen, inflammation of the joints (rheumatism), or intermittently trending skin diseases. Permanent damage to the affected organs (such as valvular heart disease) can be.
As a result of acute tonsillitis, as well as due to a chronic tonsillitis abscesses can form as a complication. This pus in the surrounding tissues accumulates. This is called a peritonsillar abscess. Indications for this are strong pain of swallowing up to the inability of swallowing, a painful, difficult mouth opening (so-called pine Terminal), as well as an irregular protrusion of the soft palate. The tonsils are swollen so strongly that they displace the Uvula to the opposite side. A danger is that the germs in the bloodstream to reach and can spread throughout the body (sepsis). This can lead to severe ailments in other organs. Therefore must be operated in most cases in the short term, if formed an abscesses.
Tonsillitis (tonsillitis, angina tonsilaris): prevention
(Tonsillitis, angina tonsillaris) you can only indirectly prevent a tonsillitis. Through regular sports and a balanced and vitamin rich diet to strengthen your immune system. To reduce the risk on a tonsillitis to fall ill.
In addition, you should avoid substances that irritate the mucous membranes. These include, inter alia, cigarette smoke, dust, and alcohol.