 Called Inflammatory markers – also inflammatory markers – are blood values, with which you can search ungezielt for inflammation in the body. They can also be used to monitor the history of an inflammatory disease.
Called Inflammatory markers – also inflammatory markers – are blood values, with which you can search ungezielt for inflammation in the body. They can also be used to monitor the history of an inflammatory disease.
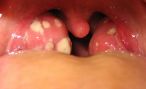
Therefore, the review of a blood sample on Inflammatory markers on suspicion of an infection often among the first steps taken to diagnose. The inflammatory markers include the following blood values: the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP) and number of white blood cells (leukocytes) – any increase of these values is a possible signs of inflammation. To determine a higher count (so called Leukocytosis), the doctor makes a small blood count.
In addition to the blood result indicating Entzündungsmarker information about this other findings may indicate inflammatory processes in the body. Other inflammatory parameters are, for example, the body temperature and the number of leukocytes in urine, cerebrospinal fluid, or Chair.
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
A possible sign of inflammation in the body – and thus a Inflammatory markers – is the erythrocyte sedimentation rate or blood sedimentation rate (ESR). To determine it draws to blood in a tube and prepares this vertically. The fixed components of blood, so the blood cells fall attracted – on the floor of the tube then slowly – by gravity. After an hour, we read off how far the blood cells have fallen.
The rate is particularly dependent on the surface of blood cells. Proteins, which are the blood cells stick together, can be found in the blood increased the blood sedimentation rate is increased. This is the case with inflammation. But this Entzündungsmarker alone is still no secure evidence of inflammation: other factors such as anemia (anemia) can also affect the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and exceed the normal values.
Principle: an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is an indication of inflammation. However, the values for these Entzündungsmarker also in healthy individuals or by other, non-inflammatory diseases can be increased.
Possible causes for an increase include BSG in healthy subjects:
- Menstruation
- Taking hormonal contraception (so-called pill)
- Pregnancy
Possible reasons for an increase in the BSG in patients are:
- Infections (infectious and non-infectious), for example thyroid inflammation
- Cancer patients, for example plasmacytoma
- Auto-immune diseases
- Kidney disease, such as the nephrotic syndrome or renal failure
- Blood disorders (anemia, leukemia, Hämolysen)
- Chronic liver disease, for example liver cirrhosis
- Rheumatic diseases such as the rheumatoid arthritis
C-reactive protein
A Entzündungsmarker faster response when compared to the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is the C reactive protein (CRP): C-reactive protein increases to about six to ten hours after the start of the disease in the blood. In addition, the CRP values normalize after the disease more quickly (after about two weeks) as the BGS. Therefore, the C reactive protein in the diagnosis of acute infections of as Entzündungsmarker BSG is superior. Only in autoimmune diseases it can happen that the value of CRP in the blood is increased little or not, while the BSG is almost always faster.
C-reactive protein (CRP) is one of the so-called acute phase proteins. His education takes place in the liver: in the course of inflammation, the white blood cells (leukocytes) – the macrophages and granulocytes – directly involved in the inflammatory response pour out messengers. These messengers (called cytokines) circulate in the blood and throw in the liver a reaction, in which the liver pours out the Entzündungsmarker.